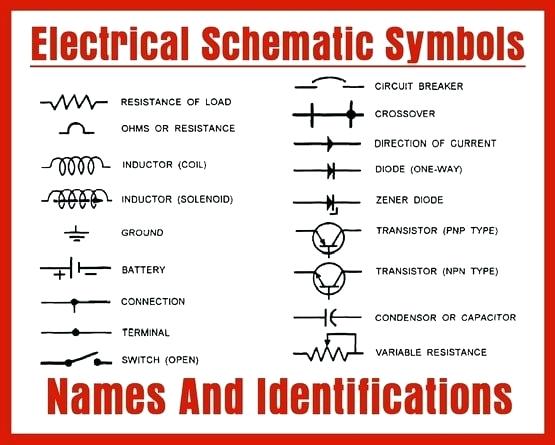
Basic Electrical Symbols
Let’s go over some sample electrical symbols and what they represent.
Ground or Earth
A ground symbol (IEC symbol 5017) identifies a ground terminal. It can be used for a zero potential reference point from where current is measured. It is also for electrical shock protection. There are a few different ground symbols. The one we’re showing here is “Earth”, but there’s also a Chassis and Digital/Common ground with slight variations to this symbol.
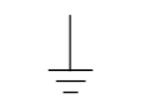
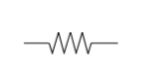
Resistor
A resistor reduces current flow. In a schematic, this is represented with a few zig zag squiggles. We’re showing the US/Japan version of this symbol (IEEE). The UK uses a simple box over a straight line (IEC). There are also symbols for variable and adjustable resistors as well as thermal and preset resistors.
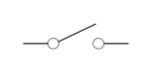
Switch
Disconnects the current when open. We’re showing a simple SPST (single-pole single-throw) toggle switch, but there are variations for SPDT, pushbutton, dip, relay, and more. For a complete list of switch symbols, check out SmartDraw’s electrical symbol library.
Capacitor
A capacitor symbol shows two terminals running into plates. The curved plate indicates that the capacitor is polarized. The curved side has lower voltage. A small plus sign can be added to the straight side indicated the positive pin.
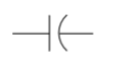
Fuse
A fuse protects electrical circuits by stopping the flow of current when the intensity of current exceed a set value. It does this by melting a special wire.

Antenna
Marks a device, rod, or wire designed to capture radio and electromagnetic waves into electrical signals and vice versa.

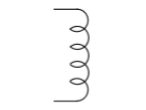
Inductor
An inductor is also called a coil or reactor. The coils store energy in a magnetic field or flux. An inductor symbol looks like a series of looped coils.
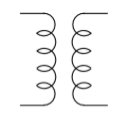
Transformer
A transformer is two or more coils coupled by magnetic induction. It helps keep the frequency and reduce tension in an AC circuit.
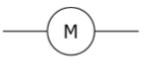
Motor
A motor is a device that can transform electric energy into mechanical energy.
Source
Represents the power source for your electronics. This symbol represent a direct current (DC). To represent AC current, you’d replace the plus and minus sign with a wave.

Battery
Batteries are represented on a schematic with a pair of disproportionate, parallel lines. The number of lines indicates the number of series cells in the battery.
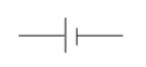
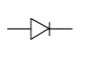
Diode
A diode only allows current to flow in one direction. It’s always polarized with an anode (A, positive) and cathode side (C, negative).
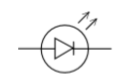
Diode LED
A diede LED is a standard diode symbol with two small arrows showing the emission of light.